- October 1, 2025
- linkzeeshan.ayyub
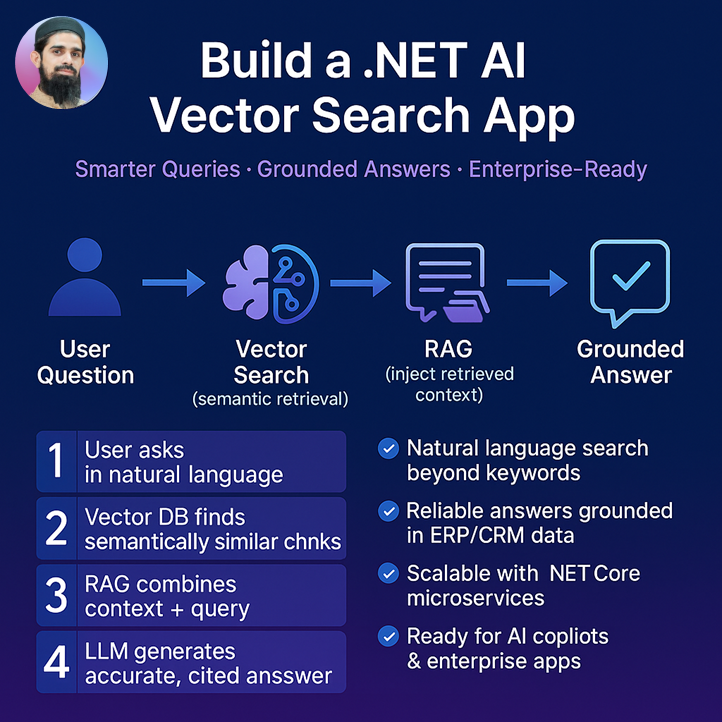
What is RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation)?
RAG = Retrieval + Generation
It is a method where you combine your data (retrieval) with a Large Language Model (LLM, e.g., GPT-4) to get accurate, grounded answers.
- Retrieval Step (your guess is correct )
- “Retrieval” means: fetching relevant data from a database or knowledge store.
- This is not just any database — it’s usually a vector database (pgvector, Pinecone, Chroma, Qdrant).
- Why vector DB? Because LLMs work with semantic meaning, not just exact keywords.
Example:
You have your company documents (ERP policies, manuals, FAQs).
- You split them into chunks.
- Convert each chunk into a vector (embedding).
- Store vectors + metadata in a vector DB.
Now, when the user asks:
“What is the lead time for raw material supply?”
- The system creates a vector for the query.
- Vector DB finds the most relevant chunks from your documents (maybe a PDF policy that says “lead time is 10 days”).
- That’s the retrieval step.
- Augmented Generation Step
- After retrieval, the system augments the user’s query with the retrieved context.
- Then it sends both → the LLM (e.g., GPT-4).
- The LLM generates an answer but stays grounded in the retrieved text.
Example continued:
Context retrieved = “Raw material supply lead time is 10 days (per ERP configuration)”
User question = “What is the lead time for raw material supply?”
Prompt to GPT becomes:
Use this context to answer the user:
“Raw material supply lead time is 10 days (per ERP configuration).”
User Question: What is the lead time for raw material supply?
LLM Answer:
“The lead time for raw material supply is 10 days, as per ERP records.”
- Database: Yours or Others?
- Mostly YOUR database / documents:
- PDFs, manuals, ERP tables, FAQs, tickets, product catalogs.
- Sometimes external knowledge:
- Public knowledge bases (Wikipedia, scientific papers).
- APIs (financial data, stock prices).
💡 Key point: RAG lets you inject YOUR domain knowledge into an LLM that otherwise only knows its training data (up to a cutoff date).
- Simple Analogy
Think of GPT as a very smart student but with no access to your company notes.
- If you ask without RAG → he will guess (hallucinate).
- With RAG → first hand him your company notes (retrieval), then ask the question.
- He now answers accurately using your notes.
✅ So yes, your understanding is right:
- Retrieval = fetch relevant data from a knowledge store (which can be your database).
- RAG = use that data to guide the LLM’s generation.
ERP RAG Example – Step by Step
- Store your company knowledge
Take ERP data and documents, break into chunks, embed into a vector DB:
- Inventory: stock levels, safety stock thresholds.
- Production: machine capacity, shift schedules.
- Energy: boiler/chiller logs, energy KPIs.
👉 Example chunk (from doc or DB row):
“POY yarn minimum safety stock is 1000 kg. Current stock = 750 kg. Lead time for replenishment = 10 days.”
Embedding model → [0.24, -0.19, 0.87, …] → stored in vector DB.
- User asks a question
ERP user types:
“Do we have enough POY yarn to meet export order next week?”
- Retrieval step
- System turns question → vector.
- Queries vector DB.
- Finds chunks like:
- Stock data: “Current stock = 750 kg”
- Order data: “Export order requires 1000 kg in 7 days”
- Safety stock rules: “Safety stock threshold = 1000 kg”
- Augmented prompt to GPT
Prompt builder creates this:
You are an ERP assistant.
Use ONLY the context below to answer.
If context is insufficient, say “I don’t know.”
Context:
- Current stock of POY yarn = 750 kg.
- Export order requires 1000 kg due in 7 days.
- Safety stock threshold = 1000 kg.
- Lead time for replenishment = 10 days.
User Question:
Do we have enough POY yarn to meet the export order next week?
- LLM (Generation step)
GPT responds:
“No. Current stock (750 kg) is below the required export order (1000 kg) and also below the safety stock threshold (1000 kg). Since replenishment lead time is 10 days, the order cannot be fulfilled on time unless stock is expedited.”
Why RAG Matters in ERP
- Without RAG → GPT might guess or hallucinate.
- With RAG → Answer is grounded in real ERP data.
- This is how you build AI copilots for ERP: Chat-like interface that always checks facts against your database before answering.
ERP-Specific Use Cases for RAG
- Inventory Q&A → “What’s our current PSF stock and when will it fall below threshold?”
- Production scheduling → “Which machines are available to run FDY order this weekend?”
- Energy efficiency → “Which chiller is showing abnormal consumption this month?”
- Demand forecasting explanation → “Why did the system forecast a spike in POY demand?” (model + retrieved logs).
That’s RAG: Retrieval = ERP facts, Generation = GPT explanation.