In this article following point we will discuss:
Performance issue with single queries:
Single query performance issues arise from complex object graphs, large datasets, and unnecessary data retrieval, resulting in increased memory usage and longer execution times.
Example:
you’re working with a large database of information, like a huge library of books. When you use single queries in Entity Framework Core, it’s like trying to find all the information you need from that library in one go. However, if the library is big and the information is spread out across many books, it can take a lot of time and effort to gather everything you need.
Let’s examine the following LINQ query and its translated SQL equivalent:
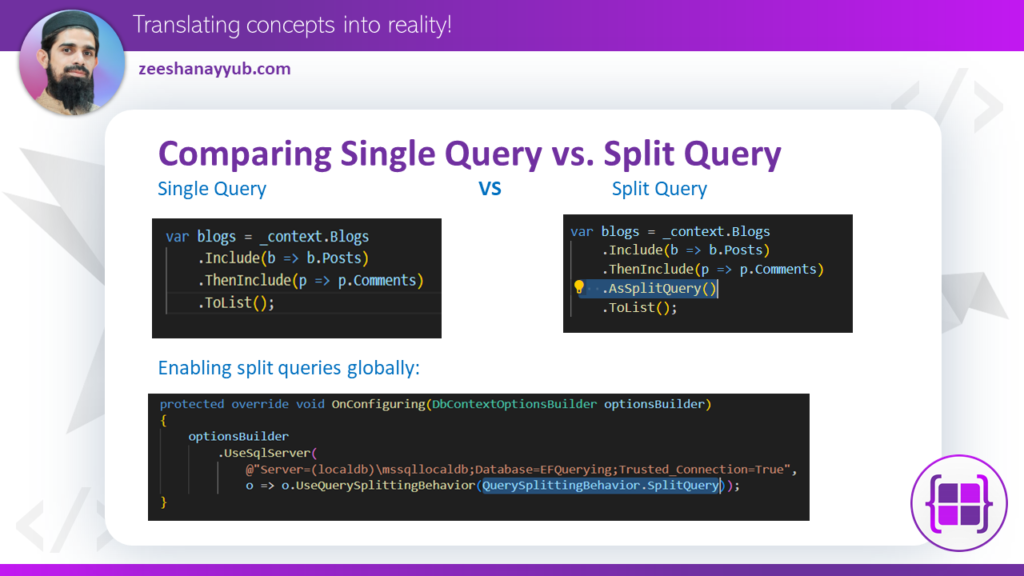
var blogs = ctx.Blogs
.Include(b => b.Posts)
.Include(b => b.Contributors)
.ToList();
It will produce the following SQL:
SELECT [b].[Id], [b].[Name], [p].[Id], [p].[BlogId], [p].[Title], [c].[Id], [c].[BlogId], [c].[FirstName], [c].[LastName]
FROM [Blogs] AS [b]
LEFT JOIN [Posts] AS [p] ON [b].[Id] = [p].[BlogId]
LEFT JOIN [Contributors] AS [c] ON [b].[Id] = [c].[BlogId]
ORDER BY [b].[Id], [p].[Id]
Split Queries:
Split queries in Entity Framework Core split the workload between your client and the database, helping fetch data more efficiently, especially when tasks are complex or need some processing on your client ‘s side.
Example:
Split queries in Entity Framework Core are like teamwork in a library: tasks are divided between the database and the application, making data retrieval faster. It’s akin to different people searching different sections of a library, making the process more efficient and manageable.
var blogs = context.Blogs
.Include(blog => blog.Posts)
.AsSplitQuery()
.ToList();
It will produce the following SQL:
SELECT [b].[BlogId], [b].[OwnerId], [b].[Rating], [b].[Url]
FROM [Blogs] AS [b]
ORDER BY [b].[BlogId]
SELECT [p].[PostId], [p].[AuthorId], [p].[BlogId], [p].[Content], [p].[Rating], [p].[Title], [b].[BlogId]
FROM [Blogs] AS [b]
INNER JOIN [Posts] AS [p] ON [b].[BlogId] = [p].[BlogId]
ORDER BY [b].[BlogId]
Enabling split queries globally:
Enabling split queries globally configures the database context in Entity Framework Core to efficiently divide query tasks between the application and the database, enhancing overall performance and data retrieval efficiency.
You can also configure split queries as the default for your application’s context:
protected override void OnConfiguring(DbContextOptionsBuilder optionsBuilder)
{
optionsBuilder
.UseSqlServer(
@"Server=(localdb)\mssqllocaldb;Database=EFQuerying;Trusted_Connection=True",
o => o.UseQuerySplittingBehavior(QuerySplittingBehavior.SplitQuery));
}